The idea of a resource is an abstract one using Generic Foreign Key and not a concrete one with a model.
9.3 KiB
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
This document describes the RBAC implementation of the Ansible Tower Software. The intended audience of this document is the Ansible Tower developer.
Overview
RBAC - System Basics
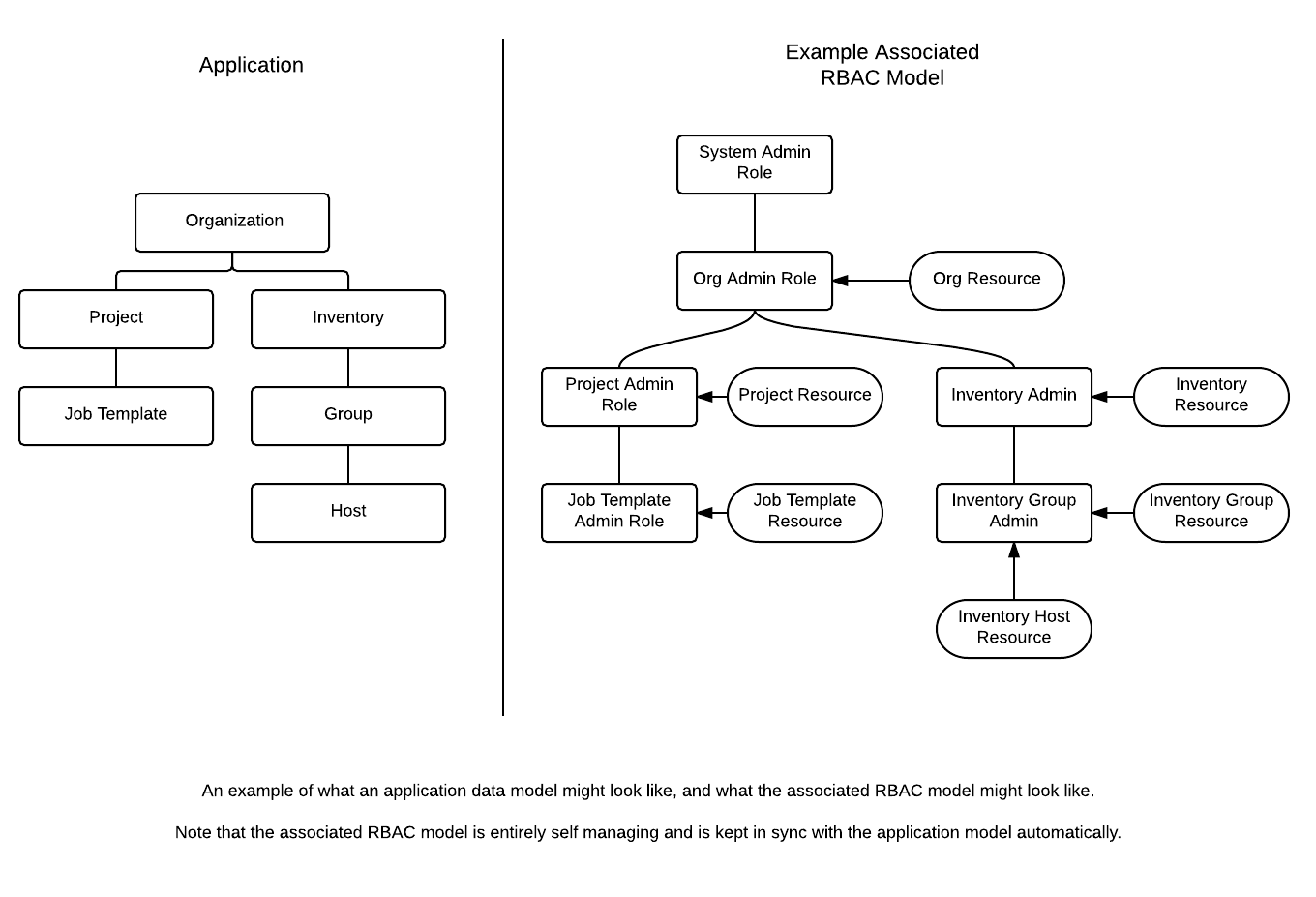
There are four main concepts to be familiar with, Roles, Resources, Users, and Permissions. Users can be members of a role, which gives them access to any permissions bestowed upon that Role. In order to access a Resource, a Permission must be granted to a Role enabling all members of that Role to access the Resource.
For example, if I have an organization named "MyCompany" and I want to allow two people, "Alice", and "Bob", access to manage all the settings associated with that organization, I'd create a role (maybe called "MyCompany Administrator"), create a Permission to edit the organization "MyCompany" and assign it to the "MyCompany Administrator" role. I'd also add the two users "Alice" and "Bob" as members of the Role.
It is often the case that you have many Roles in a system, and you want some roles to include all of the permissions of other roles. For example, you may want a System Administrator to have access to everything that an Organization Administrator has access to, who has everything that a Project Administrator has access to, and so on. We refer to this concept as the 'Role Hierarchy', and is represented by allowing Roles to have "Parent Roles". Any permission that a Role has is implicitly granted to any parent roles (or parents of those parents, and so on). Of course Roles can have more than one parent, and permissions are implicitly granted to all parents. (Technically speaking, this forms a directional graph instead of a hierarchy, but the concept should remain intuitive.)
Implementation Overview
The RBAC system allows you to create and layer roles for controlling access to resources. Any Django Model can
be made into a resource in the RBAC system by using the ResourceMixin. Once a model is accessible as a resource you can
extend the model definition to have specific roles using the ImplicitRoleField. This role field allows you to
configure the name of a role, any parents a role may have, and the permissions this role will grant to members.
Roles
Roles are defined for a resource. If a role has any parents, these parents will be considered when determining what roles are checked when accessing a resource.
ResourceA
|-- AdminRole
ResourceB
| -- AdminRole
|-- parent = ResourceA.AdminRole
When a user attempts to access ResourceB we will check for their access using the set of all unique roles, including the parents.
ResourceA.AdminRole, ResourceB.AdminRole
This would provide any members of the above roles with access to ResourceB.
Singleton Role
There is a special case Singleton Role that you can create. This type of role is for system wide roles.
Models
The RBAC system defines a few new models. These models represent the underlying RBAC implementation and generally will be abstracted away from your daily development tasks by the implicit fields and mixins.
Role
Role defines a single role within the RBAC implementation. It encapsulates the ancestors, parents, and members for a role. This model is intentionally kept dumb and it has no explicit knowledge of a Resource. The Role model (get it?), defines some methods that aid in the granting and creation of roles.
visible_roles(cls, user)
visible_roles is a class method that will lookup all of the Role instances a user can "see". This includes any roles the user is a direct decendent of as well as any ancestor roles.
singleton(cls, name)
The singleton class method is a helper method on the Role model that helps in the creation of singleton roles. It will return the role by name if it already exists or create and return the new role in the case it does not.
get_absolute_url(self)
get_absolute_url returns the consumable URL endpoint for the Role.
rebuild_role_ancestor_list(self)
rebuild_role_ancestor_list will rebuild the current role ancestory that is stored in the ancestors field of a Role. This is called for you by save and different Django signals.
is_ancestor_of(self, role)
is_ancestor_of returns if the given role is an ancestor of the current Role instance.
RolePermission
RolePermission holds unique role_permissions. You interact with this model indirectly when declaring ImplicitRoleField fields. Generally you will not directly use this model unless you are extending the RBAC implementation itself.
Fields
ImplicitRoleField
ImplicitRoleField fields are declared on your model. They provide the definition of grantable roles for accessing your resource. Configuring the role is done using some keyword arguments that are provided during declaration.
parent_role is the link to any parent roles you want considered when a user is requesting access to your resource. A parent_role can be declared as a single string, parent.readonly, or a list of many roles, ['parentA.readonly', 'parentB.readonly']. It is important to note that a user does not need a parent role to access a resource if granted the role for that resource explicitly. Also a user will not have access to any parent resources by being granted a role for a child resource. We demonstrate this in the Usage section of this document.
role_name is the display name of the role. This is useful when generating reports or looking the results of queries.
permissions can be used when the model that contains the
ImplicitRoleField utilizs the ResourceMixin. When present, a
RolePermission entry will be automatically created to grant the specified
permissions on the resource to the role defined by the ImplicitRoleField.
This field should be specified as a dictionary of permissions you wish to
automatically grant. Below is a list of available permissions. The special
permission all is a shortcut for generating a dict with all of the explicit
permissions listed below set to True. Note that permissions default to
False if not explicitly provided.
# Available Permissions
{'create':True, 'read':True, 'write':True, 'update':True,
'delete':True, 'scm_update':True, 'use':True, 'execute':True}
# Special Permissions
{'all':True}
# Example: readonly
{'read':True}
Mixins
ResourceMixin
By mixing in the ResourceMixin to your model, you are turning your model in to a resource in the eyes of the RBAC implementation. Your model will gain the helper methods that aid in the checking the access a users roles provides them to your resource.
accessible_objects(cls, user, permissions)
accessible_objects is a class method to use instead of Model.objects. This method will restrict the query of objects to only the objects that a user has the given permissions for. Note that any permission fields that are left blank will default to False. accessible_objects will only filter out resources where the expected permission was True but was returned as False.
objects = Model.accessible_objects(user, {'write':True})
objects.filter(name__istartswith='december')
get_permissions(self, user)
get_permissions is an instance method that will give you the permission dictionary for a given user. This permission dictionary will take in to account any parent roles the user is apart of.
>>> instance.get_permissions(admin)
{'create':True, 'read':True, 'write':True, 'update':True,
'delete':True, 'scm_update':True, 'execute':True, 'use':True}
accessible_by(self, user, permissions)
accessible_by is an instance method that wraps the get_permissions method. Given a user and a dictionary of permissions this method will return True or False if a users roles give them a set of permissions that match the provided permissions dictionary. Note that any permission fields left blank will default to False. accessible_by will only return False in a case where the passed in permission is expected to be True but was returned as False.
>>> instance.accessible_by(admin, {'use':True, 'read':True})
True
Usage
After exploring the Overview the usage of the RBAC implementation in your code should feel unobtrusive and natural.
# make your model a Resource
class Document(Model, ResourceMixin):
...
# declare your new role
readonly_role = ImplicitRoleField(
role_name="readonly",
permissions={'read':True},
)
Now that your model is a resource and has a Role defined, you can begin to access the helper methods provided to you by the ResourceMixin for checking a users access to your resource. Here is the output of a Python REPL session.
# we've created some documents and a user
>>> document = Document.objects.filter(pk=1)
>>> user = User.objects.first()
>>> document.accessible_by(user, {'read': True})
False # not accessible by default
>>> document.readonly_role.memebers.add(user)
>>> document.accessible_by(user, {'read':True})
True # now it is accessible
>>> document.accessible_by(user, {'read':True, 'write':True})
False # my role does not have write permission