3.3 KiB
| title | description |
|---|---|
| Concepts | Traefik - base concepts and main features |
Concepts
This page explains the base concepts of Traefik.
Introduction
Traefik is based on the concept of EntryPoints, Routers, Middlewares and Services.
The main features include dynamic configuration, automatic service discovery, and support for multiple backends and protocols.
-
EntryPoints: EntryPoints are the network entry points into Traefik. They define the port which will receive the packets, and whether to listen for TCP or UDP.
-
Routers: A router is in charge of connecting incoming requests to the services that can handle them.
-
Middlewares: Attached to the routers, middlewares can modify the requests or responses before they are sent to your service
-
Services: Services are responsible for configuring how to reach the actual services that will eventually handle the incoming requests.
Edge Router
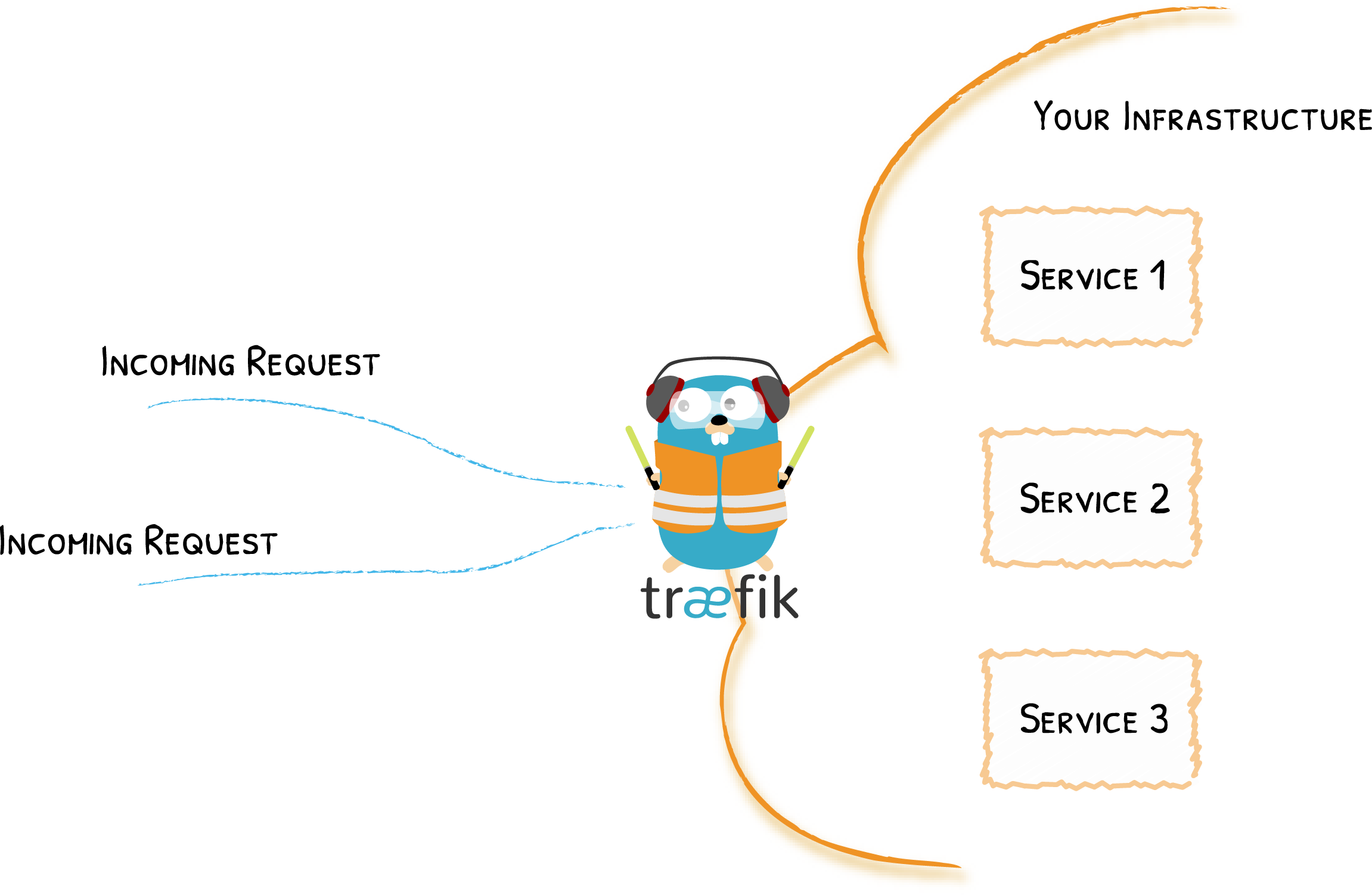
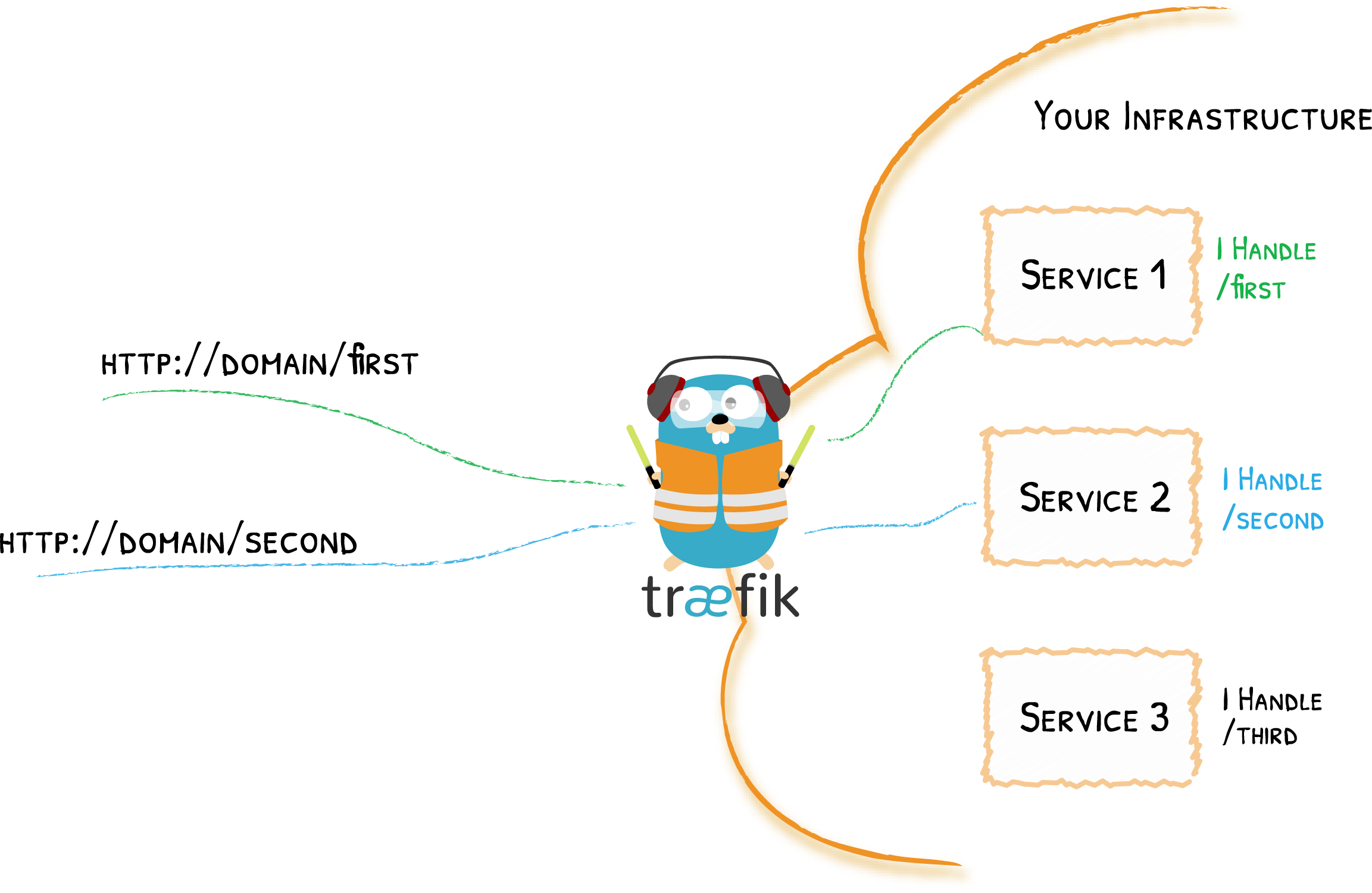
Traefik is an Edge Router; this means that it's the door to your platform, and that it intercepts and routes every incoming request: it knows all the logic and every rule that determine which services handle which requests (based on the path, the host, headers, etc.).
Auto Service Discovery
Where traditionally edge routers (or reverse proxies) need a configuration file that contains every possible route to your services, Traefik gets them from the services themselves.
Deploying your services, you attach information that tells Traefik the characteristics of the requests the services can handle.
This means that when a service is deployed, Traefik detects it immediately and updates the routing rules in real time. Similarly, when a service is removed from the infrastructure, the corresponding route is deleted accordingly.
You no longer need to create and synchronize configuration files cluttered with IP addresses or other rules.
!!! info "Many different rules"
In the example above, we used the request [path rule](../routing/routers/index.md#rule "Link to docs about routing rules") to determine which service was in charge.
Certainly, you can use many other different [rules](../routing/routers/index.md#rule "Link to docs about routing rules").
!!! info "Updating the requests"
In the [middleware](../middlewares/overview.md "Link to middleware documentation") section, you can learn about how to update the requests before forwarding them to the services.
!!! question "How does Traefik discover the services?"
Traefik is able to use your cluster API to discover the services and read the attached information.
In Traefik, these connectors are called [providers](../providers/overview.md "Link to overview about Traefik providers") because they *provide* the configuration to Traefik.
{!traefik-for-business-applications.md!}